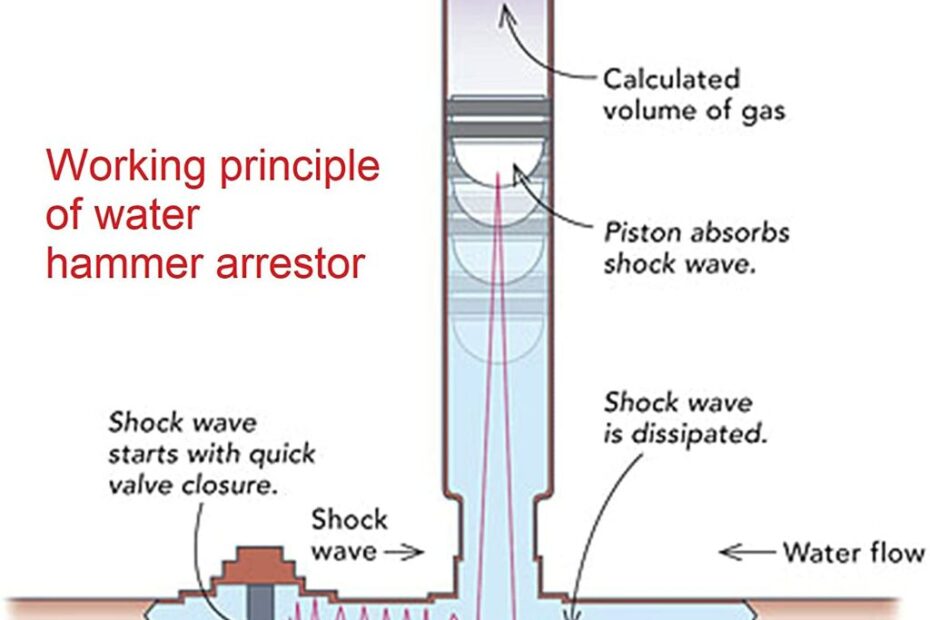
Water hammer arrestors are essential components in modern plumbing systems, designed to prevent the damaging effects of water hammer – a phenomenon that occurs when flowing water suddenly stops or changes direction. These devices protect pipes, fittings, and appliances while ensuring quiet operation of the plumbing system.
Understanding Water Hammer
Water hammer occurs in closed pipes when fluid is rapidly accelerated or decelerated, typically due to quick valve closures or pump operations[1]. This sudden change creates pressure waves that propagate through the system, causing distinctive banging noises and potentially damaging vibrations.
The Physics Behind Water Hammer
When water flowing at 60-70 psi suddenly stops, it creates a pressure surge that can be 3-5 times higher than the normal supply pressure[3][4]. This energy must be dissipated somewhere in the system, and without proper protection, it results in:
- Pipe vibration and movement
- Stress on joints and fittings
- Potential system damage
- Loud banging noises
How Water Hammer Arrestors Function
A water hammer arrestor operates like a shock absorber in a vehicle, using a sealed chamber filled with air or gas and a piston to cushion pressure waves[2]. The device consists of two main chambers:
Primary Components
- A cylinder divided into two chambers
- A piston with O-ring seals
- A closed air chamber for dampening
- A water chamber connected to the pipe
- A contrast spring behind the piston[1]
Operation Process
- During normal flow, the piston remains in its neutral position
- When water hammer occurs, the pressure wave enters the water chamber
- The piston compresses the air chamber, absorbing the shock
- The spring assists in returning the piston to its original position
- The cycle repeats as needed for subsequent pressure waves
Types of Water Hammer Arrestors
Modern plumbing systems utilize several different types of water hammer arrestors, each designed for specific applications and pressure requirements.
Air Chamber Arrestors
The simplest and most traditional type, air chamber arrestors consist of a vertical pipe extension filled with air. While economical, they have limitations:
- Air can become waterlogged over time
- Requires periodic draining and refilling
- Less effective than mechanical alternatives
- Limited pressure absorption capacity
Mechanical Piston Arrestors
These represent the most common modern solution, featuring a sliding piston that separates water from a permanent air chamber:
Advantages:
- Permanent seal prevents air absorption
- Maintenance-free operation
- Precise pressure rating options
- Long service life
Applications:
- Residential plumbing systems
- Commercial installations
- Industrial processes
- Quick-closing valve protection
Bladder-Style Arrestors
Using an elastic membrane instead of a piston, these devices offer unique benefits:
- Superior shock absorption
- No mechanical parts to wear
- Excellent for high-pressure systems
- Enhanced durability in extreme conditions
Installation Considerations
Proper installation is crucial for optimal performance. Key factors include:
Placement Guidelines
- Install as close as possible to the source of water hammer
- Mount in vertical position when possible
- Ensure accessibility for maintenance
- Consider multiple arrestors for complex systems
Sizing Requirements
| Fixture Type | Recommended Arrestor Size |
|---|---|
| Washing Machine | 2.0 cubic inches |
| Dishwasher | 1.5 cubic inches |
| Quick-closing Valve | 1.0 cubic inches |
| Multiple Fixtures | 3.0+ cubic inches |
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity of water hammer arrestors. While modern mechanical arrestors are generally maintenance-free, regular inspection is recommended.
Common Issues and Solutions
Air Chamber Problems:
- Waterlogging: Requires system drainage and air recharge
- Corrosion: May need replacement after 5-7 years
- Incorrect sizing: Results in reduced effectiveness
- Installation errors: Can lead to premature failure
Performance Monitoring
Regular system checks should include:
- Listening for water hammer sounds
- Checking for visible pipe movement
- Inspecting for leaks around arrestor connections
- Verifying proper mounting and support
Professional Standards and Regulations
Water hammer arrestors must comply with various industry standards and building codes:
Certification Requirements
- PDI-WH 201: Performance standard for water hammer arrestors
- ASSE 1010: Performance requirements for mechanical devices
- ANSI A112.26.1: Installation and testing specifications
Installation Codes
Building codes typically require water hammer arrestors in:
- Quick-closing valve locations
- Solenoid valve applications
- High-pressure systems
- Multiple fixture installations
Design Considerations
Engineers must consider several factors when selecting and implementing water hammer arrestors:
System Analysis
- Flow rates and velocities
- Operating pressures
- Valve closure times
- Pipe material and size
- Temperature variations
Pressure Calculations
The maximum surge pressure can be calculated using the formula:
P = (0.070)(V)(c)/g
Where:
- P = Surge pressure (psi)
- V = Flow velocity (ft/sec)
- c = Wave velocity (ft/sec)
- g = Gravitational constant
Advanced Applications and Innovations
Modern water hammer arrestor technology continues to evolve, incorporating new materials and design features for enhanced performance.
Smart Monitoring Systems
Recent innovations include:
- Integrated pressure sensors
- Digital monitoring capabilities
- Remote system alerts
- Predictive maintenance features
Industrial Applications
Heavy-duty arrestors for industrial use offer:
- Higher pressure ratings (up to 3000 psi)
- Temperature compensation
- Chemical resistance
- Extended service life
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Water hammer arrestors contribute to sustainable plumbing practices through:
Energy Conservation
- Reduced system stress
- Lower maintenance requirements
- Extended equipment lifespan
- Decreased water waste from failures
Material Considerations
Modern manufacturers focus on:
- Recyclable components
- Lead-free materials
- Eco-friendly production processes
- Sustainable packaging
Cost Analysis
Investment in water hammer arrestors provides significant long-term benefits:
Initial Costs vs. Long-term Savings
| Factor | Without Arrestor | With Arrestor |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Lifespan | 5-7 years | 10-15 years |
| Maintenance Costs | High | Minimal |
| Repair Frequency | Regular | Rare |
| System Efficiency | Decreased | Optimal |
Return on Investment
Typical savings include:
- Reduced repair costs
- Lower insurance premiums
- Extended equipment life
- Decreased water damage risk
Future Developments
Emerging trends in water hammer arrestor technology include:
- Smart home integration
- IoT connectivity
- Advanced materials
- Improved efficiency designs
Key Takeaways
Water hammer arrestors are crucial components that protect plumbing systems from pressure surges, extending system life and preventing damage. Their proper selection, installation, and maintenance ensure optimal performance and system protection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How long do water hammer arrestors last?
A: Quality mechanical water hammer arrestors typically last 10-15 years under normal conditions. However, traditional air chambers may require maintenance every 3-5 years.
Q: Can I install a water hammer arrestor myself?
A: While DIY installation is possible for simple applications, professional installation is recommended to ensure proper sizing, placement, and compliance with local codes.
Q: Do I need water hammer arrestors on all fixtures?
A: No, arrestors are primarily needed for quick-closing valves and appliances like washing machines, dishwashers, and solenoid-operated devices.
Q: How do I know if my water hammer arrestor is failing?
A: Signs of failure include returning water hammer noise, visible pipe movement, leaks around the arrestor, and unusual system sounds.
Q: Can water hammer arrestors be installed horizontally?
A: While vertical installation is preferred, many modern arrestors can be installed horizontally. Always check manufacturer specifications for proper orientation.
Q: Are water hammer arrestors required by code?
A: Many local building codes require water hammer arrestors for specific applications, particularly in new construction and major renovations.
Final Thoughts
Water hammer arrestors represent a critical component in modern plumbing systems, offering protection against potentially damaging pressure surges. Understanding their operation, selection, and maintenance requirements ensures optimal system performance and longevity. As technology continues to advance, these devices will become increasingly sophisticated, offering enhanced protection and monitoring capabilities for both residential and industrial applications.
Citations:
[1] https://www.caleffi.com/sites/default/files/media/external-file/01020_EN.pdf
[2] https://maheshvalves.com/understanding-water-hammer-arrestors-causes-effects-and-solutions/
[3] https://www.oatey.com/faqs-blog-videos-case-studies/blog/how-do-water-hammer-arrestors-work
[4] https://lehryvalves.com/water-hammering-surge-arresters-a-case-study/
[5] https://www.reddit.com/r/SEO/comments/cvp43j/advantage_of_pipes_in_title_tags/
[6] https://www.val-technik.com.sg/post/arresting-water-hammering
[7] https://www.webfx.com/industries/local-consumer-services/water-treatment/seo/